
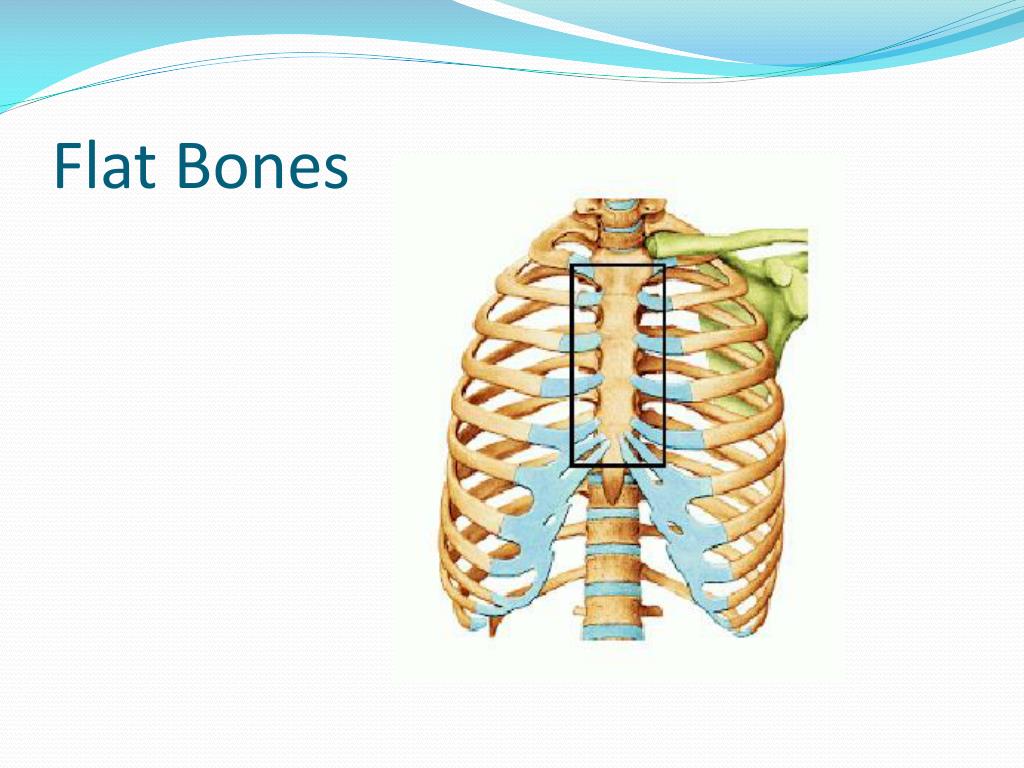
Red marrow, which produces red blood cells, platelets and most white blood cells, is usually found in the cancellous regions of flat bones such as the hip, breastbone and shoulder blades.įrom an engineering perspective, the upper arm (humerus), forearm (radius), thigh (femur) and shin (tibia) are hollow, thick-walled tubes that can be used as levers to apply force or as columns to support weight. Nerve pathways and blood vessels wind their way through the honeycomb, providing sensation and nourishment to the bone tissue. Beneath the cortex lies cancellous bone, a honeycombed network of intersecting plates and cross-braced struts (called trabeculae) that greatly reinforces the shell against external mechanical forces.

The exterior, called the cortex, consists of a dense smooth layer of bone that acts as an extremely hard shell. And so on.ĭespite their variety, bones share a common internal anatomy. The pelvis is designed for walking upright. The helmet-shaped cranium protects the delicate brain inside. Anatomy of Long Bonesįor the 206 bones that comprise the adult skeleton, form follows function: The broad flat plates of our shoulder blades are there to anchor some of the different muscle groups that give the shoulder such freedom of movement.

A broken bone, bone fracture, crack in bone, stress break, are often synonymous terms to refer to a structural break in the integrity of a bone.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
